Unlocking Efficiency and Streamlining Operations with ERP
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, staying competitive requires more than just a great product or service. It demands efficient operations, streamlined processes, and real-time data visibility. That’s where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) comes into play.
ERP is a comprehensive software solution that integrates various business functions into a single system. From finance and accounting to inventory management, supply chain, human resources, and customer relationship management (CRM), ERP centralizes all essential data and processes in one place. This unified approach enables businesses to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and make informed decisions.
One of the key benefits of implementing an ERP system is improved efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks and eliminating manual data entry, employees can focus on more value-added activities. With streamlined processes and reduced paperwork, businesses can experience faster turnaround times, reduced errors, and increased productivity across departments.
Furthermore, ERP provides real-time visibility into critical business information. Managers can access up-to-date reports and analytics to gain insights into sales trends, inventory levels, financial performance, customer behaviour, and more. This empowers decision-makers to make informed choices based on accurate data rather than relying on guesswork or outdated information.
Another advantage of ERP is its ability to enhance collaboration within an organization. With all departments working from the same system and accessing the same data source, communication barriers are broken down. This facilitates smoother coordination between teams and enables seamless sharing of information across departments. For example, sales teams can easily access inventory levels to provide accurate delivery estimates to customers while procurement teams can monitor demand patterns for better supplier management.
Moreover, ERP systems offer robust security features that protect sensitive business data from unauthorized access or breaches. With advanced user permissions and encryption protocols in place, businesses can have peace of mind knowing that their confidential information is safeguarded.
Implementing an ERP system may seem like a significant investment at first glance; however, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial costs. By streamlining operations, reducing redundancies, and improving productivity, businesses can achieve cost savings in the long run. Additionally, the scalability of ERP systems allows businesses to adapt and grow without major disruptions or additional investments in new software.
In conclusion, ERP is a powerful tool that enables businesses to unlock efficiency, streamline operations, and make data-driven decisions. With its ability to centralize processes and provide real-time visibility, ERP empowers organizations to stay competitive in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, implementing an ERP system can be a game-changer for your business success.
Frequently Asked Questions about ERP: A Comprehensive Guide for UK Businesses
- What is ERP and how does it work?
- What are the benefits of implementing an ERP system?
- How long does it take to implement an ERP system?
- How much does an ERP system cost?
- Is training required for employees when adopting an ERP system?
- Can an existing IT infrastructure integrate with an ERP system?
What is ERP and how does it work?
ERP, which stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, is a software system designed to integrate and streamline various business processes and functions within an organization. It acts as a central hub that connects different departments and enables the flow of information across the entire enterprise.
At its core, ERP works by consolidating data from different areas of the business into a unified database. This database serves as a single source of truth, ensuring that all departments have access to accurate and up-to-date information. By eliminating data silos and manual processes, ERP enables real-time visibility into key business operations.
The functionalities of an ERP system can vary depending on the specific needs of each organization. However, some common modules or components found in most ERP systems include:
- Finance and Accounting: This module handles financial transactions, accounts payable/receivable, general ledger, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources (HR): The HR module manages employee data, payroll processing, benefits administration, recruitment, training, performance evaluations, and attendance tracking.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): SCM encompasses inventory management, procurement/purchasing, order processing, demand forecasting, logistics coordination, and supplier relationship management.
- Manufacturing: This module covers production planning/scheduling, materials management (BOMs), shop floor control/tracking, quality control/assurance, and equipment maintenance.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): CRM focuses on managing customer interactions throughout the sales cycle—from lead generation to customer service—by tracking customer data, sales opportunities/pipeline management, marketing campaigns/automation.
ERP systems work by capturing data from various sources within an organization in real-time or near real-time. This data is then processed and stored in a centralized database accessible to authorized users across departments. Users can input new information or update existing records through user-friendly interfaces tailored to their specific roles.
The integrated nature of ERP allows for seamless communication between different modules or departments. For example, when a sales order is entered, it triggers updates in inventory levels, production schedules, and financial records. This ensures that all relevant parties have access to the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Moreover, ERP systems often provide reporting and analytics capabilities. Users can generate customized reports or access pre-defined dashboards to gain insights into key performance indicators (KPIs), trends, and other metrics that help in decision-making.
Overall, ERP acts as a comprehensive tool for businesses to optimize their operations by automating processes, enhancing collaboration, improving data accuracy, and enabling informed decision-making across the organization.
What are the benefits of implementing an ERP system?
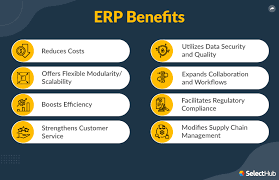
Implementing an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system can bring numerous benefits to a business. Here are some key advantages:
- Streamlined Processes: ERP integrates various business functions and processes into a single system, eliminating silos and promoting cross-departmental collaboration. This streamlines operations, reduces manual tasks, and ensures data consistency across the organization.
- Improved Efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks and eliminating manual data entry, ERP frees up employees’ time to focus on more value-added activities. This leads to increased productivity, faster turnaround times, and reduced errors.
- Real-time Data Visibility: ERP provides real-time access to critical business information through centralized databases and reporting tools. Managers can make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date data, leading to better planning, forecasting, and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Customer Service: With integrated CRM capabilities, ERP enables businesses to manage customer interactions effectively. Sales teams can access customer histories, preferences, and purchase patterns to provide personalized service and improve customer satisfaction.
- Scalability: ERP systems are designed to accommodate growth and scalability. As businesses expand or introduce new processes, an ERP system can adapt and scale accordingly without requiring significant changes or additional investments in new software.
- Cost Savings: While implementing an ERP system may involve upfront costs, it often leads to long-term cost savings. By optimizing processes, reducing redundancies, improving inventory management, and enhancing resource allocation, businesses can achieve operational efficiencies that translate into cost savings over time.
- Data Security: ERP systems offer robust security features to protect sensitive business data from unauthorized access or breaches. Advanced user permissions, encryption protocols, and regular backups ensure that confidential information remains secure.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries have specific regulatory requirements that businesses must adhere to. An ERP system can help automate compliance processes by ensuring accurate record-keeping, generating audit trails, and facilitating regulatory reporting.
- Better Decision-Making: With real-time data visibility and comprehensive reporting capabilities, ERP empowers decision-makers with actionable insights. Managers can analyze performance metrics, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to drive business growth and success.
- Improved Supply Chain Management: ERP enables businesses to optimize their supply chain by providing end-to-end visibility into inventory levels, demand patterns, and supplier performance. This helps reduce stockouts, minimize excess inventory, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
In summary, implementing an ERP system can lead to streamlined processes, improved efficiency, enhanced customer service, cost savings, better decision-making, and increased agility in a rapidly changing business environment. It is a strategic investment that can drive operational excellence and pave the way for long-term success.
How long does it take to implement an ERP system?
The implementation timeline for an ERP system can vary depending on several factors, including the complexity of the organization’s processes, the size of the business, the scope of the implementation, and the readiness of the company to embrace change. Generally, ERP implementations can take anywhere from a few months to over a year.
Here is a rough breakdown of the typical stages involved in an ERP implementation:
- Planning and Preparation: This stage involves defining project goals, selecting an appropriate ERP vendor or solution, and assembling a project team. It also includes conducting a thorough analysis of existing processes and identifying areas that need improvement.
- Customization and Configuration: During this stage, the ERP system is tailored to fit the specific needs of your organization. This may involve configuring modules, setting up workflows, defining user roles and permissions, and integrating with existing systems.
- Data Migration: Migrating data from legacy systems or spreadsheets into the new ERP system is a crucial step. It involves mapping data fields, cleaning up data inconsistencies, and ensuring data integrity during transfer.
- Testing: Rigorous testing is essential to ensure that the ERP system functions as expected and meets business requirements. This includes unit testing (individual components), integration testing (interactions between modules), and user acceptance testing (involving end-users).
- Training: Adequate training should be provided to employees who will be using the ERP system. Training sessions may cover various aspects such as navigation, data entry, reporting capabilities, and best practices.
- Go-Live: This phase marks the official launch of the ERP system for day-to-day operations. It involves migrating from old systems to using the new ERP solution entirely.
- Post-Implementation Support: After go-live, ongoing support is crucial for addressing any issues or challenges that arise during early usage stages. It may involve troubleshooting technical problems or providing additional training to users.
It’s important to note that ERP implementation is not a one-size-fits-all process, and the timeline can vary based on the complexity and customization requirements of each organization. Engaging with an experienced ERP implementation partner or vendor can help ensure a smoother and more efficient implementation process.
Remember, successful ERP implementation requires careful planning, effective project management, strong collaboration between stakeholders, and realistic expectations regarding the time required to achieve a fully functional system.
How much does an ERP system cost?
The cost of an ERP system can vary significantly depending on various factors, including the size and complexity of your business, the specific modules and functionalities required, the number of users, and whether you choose an on-premises or cloud-based solution.
For small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs), cloud-based ERP systems are often more cost-effective. These systems typically operate on a subscription-based model, where you pay a monthly or annual fee per user. The pricing can range from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars per user per year, depending on the vendor and the specific features included.
On the other hand, larger enterprises with complex operations may opt for on-premises ERP solutions. These systems involve higher upfront costs as they require purchasing licenses and hardware infrastructure. Additionally, there are ongoing costs for maintenance, upgrades, and IT support.
It’s important to note that alongside the software costs, there might be additional expenses such as implementation services, customization, data migration, training, and ongoing support. These costs can vary based on your requirements and the level of assistance needed.
To get an accurate estimate of the cost for your specific business needs, it is recommended to reach out to ERP vendors directly or consult with an ERP implementation partner who can assess your requirements and provide detailed pricing information tailored to your organization.
Remember that while cost is an important factor in decision-making, it’s equally crucial to consider the long-term benefits and return on investment (ROI) that an ERP system can deliver in terms of increased efficiency, improved productivity, better decision-making capabilities, and overall business growth.
Is training required for employees when adopting an ERP system?
Yes, training is an essential component when adopting an ERP system. Implementing a new ERP system involves a significant change in how employees perform their daily tasks and interact with the software. Thus, providing comprehensive training ensures that employees understand the functionalities of the ERP system and can utilize it effectively.
Here are a few reasons why training is necessary:
- Familiarization with the System: Training allows employees to become familiar with the new ERP software, its features, and how it integrates with their specific job roles. This includes understanding how to navigate through the system, input data, generate reports, and perform other essential tasks.
- Enhanced Productivity: Proper training ensures that employees can efficiently use the ERP system to its full potential. They will learn shortcuts, best practices, and time-saving techniques that can significantly improve productivity. With thorough training, employees can adapt quickly to the new system and minimize any disruptions during the transition period.
- Reduced Errors: Training helps employees understand data entry requirements and quality standards within the ERP system. This knowledge reduces the likelihood of errors or inconsistencies in data input, which can impact reporting accuracy and decision-making processes.
- Optimal Utilization of Features: ERP systems often have numerous features and modules designed to streamline various business processes. Through training, employees gain insights into these features and learn how to leverage them effectively for their specific job functions. This maximizes the benefits derived from implementing an ERP system.
- Change Management: Adopting an ERP system represents a significant change for employees accustomed to older processes or systems. Training plays a vital role in change management by helping employees understand why the change is happening, its benefits, and addressing any concerns or resistance they may have.
- Continuous Improvement: Training should not be viewed as a one-time event but rather as an ongoing process that supports continuous improvement within an organization’s operations. As updates or new modules are introduced in the ERP system over time, regular training sessions can keep employees up to date with the latest features and functionalities.
In summary, training is crucial when adopting an ERP system to ensure successful implementation and user adoption. It empowers employees to fully utilize the system’s capabilities, enhances productivity, reduces errors, and supports change management efforts. By investing in comprehensive training, businesses can maximize the return on their ERP investment and drive operational efficiency.
Can an existing IT infrastructure integrate with an ERP system?
Yes, an existing IT infrastructure can integrate with an ERP system. In fact, one of the key advantages of ERP is its ability to integrate and communicate with other systems within an organization.
ERP systems are designed to be flexible and adaptable, allowing for seamless integration with various components of an existing IT infrastructure. This includes integrating with databases, legacy systems, customer relationship management (CRM) software, supply chain management tools, and other business-critical applications.
Integration can be achieved through various methods such as application programming interfaces (APIs), web services, middleware solutions, or custom development. The specific integration approach will depend on the existing IT infrastructure and the capabilities of the ERP system being implemented.
By integrating an ERP system with existing IT infrastructure, businesses can leverage the data and functionalities already in place. This ensures a smooth flow of information across different systems and eliminates the need for duplicate data entry or manual synchronization.
For example, an ERP system can integrate with a CRM system to provide real-time access to customer data. This enables sales teams to view order history, track customer interactions, and provide personalized service. Similarly, integration with inventory management systems allows for accurate tracking of stock levels and automated replenishment processes.
It’s important to note that integrating an ERP system requires careful planning and consideration. Organizations should assess their existing IT landscape, evaluate compatibility between systems, define integration requirements, and establish a clear roadmap for implementation.
Working closely with experienced IT professionals or consultants who specialize in ERP implementation can help ensure a successful integration process. These experts can guide organizations through the integration journey by identifying potential challenges, recommending best practices for data migration and synchronization, and providing ongoing support.
In summary, integrating an ERP system with an existing IT infrastructure is not only possible but also highly beneficial. It enables organizations to leverage their current technology investments while gaining the advantages of a comprehensive ERP solution. With proper planning and expertise, businesses can achieve a seamless integration that optimizes their operations and maximizes the value of their IT investments.